| Type of Aluminum Door | Typical U-Value (W/m²K) | Energy Efficiency | Insulation |
| Standard Aluminum Doors | 4.5 – 5.5 | Low | / |
| Thermally Broken Aluminum Doors | 1.0 – 1.8 | Moderate | Thermal Break |
| Insulated Aluminum Doors | 0.5 – 1.0 | High | Core Insulation |
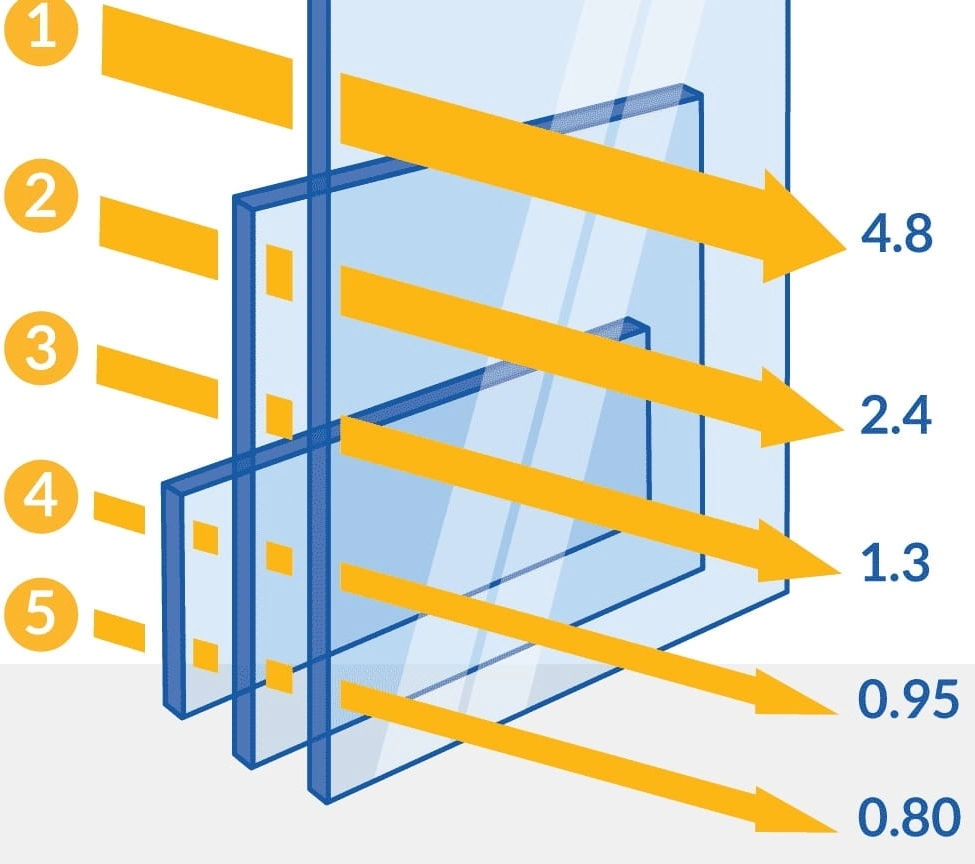
U-value measures the rate of heat transfer through materials, indicating how well a material insulates.

A lower U-value means better thermal performance, crucial for energy efficiency in aluminum door panels.
U-value is vital for energy performance, reducing heating/cooling costs, and enhancing comfort in buildings, making it a key factor when choosing aluminum doors for energy efficiency.
U-Value Standards for Aluminum Door Panels

Current U-value standards for aluminum doors vary globally.
The UK, Europe, and the US have set limits based on climate and energy efficiency goals.
New regulations like Part L in the UK enforce stricter U-value requirements for new builds, urging the use of low U-value doors for better energy performance.
Types of Aluminum Doors and Their U-Value
Let’s explore the different types of aluminum doors and how their U-values impact thermal performance.
Standard Aluminum Doors

Standard aluminum doors typically have higher U-values ranging from 4.5 to 5.5 W/m²K.
While they are durable and affordable, they lack insulation, making them less energy-efficient compared to other door types.
Thermally Broken Aluminum Doors
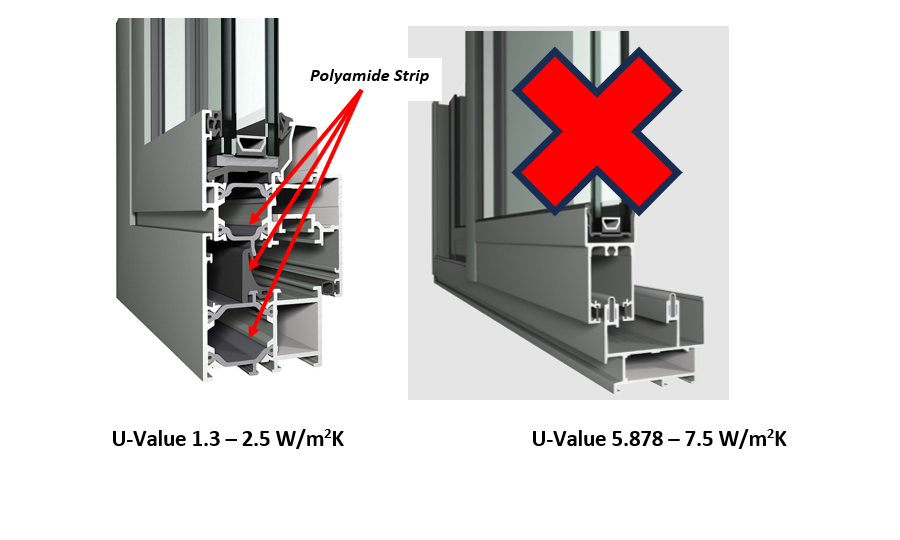
Thermally broken aluminum doors incorporate a non-conductive material between the frame’s inner and outer sections, reducing heat transfer.
These doors generally achieve U-values ranging from 1.0 to 1.8 W/m²K, offering better insulation than standard doors.
Insulated Aluminum Doors

Insulated aluminum doors are the most energy-efficient option, featuring core materials like polyurethane or polystyrene.
These doors can achieve U-values as low as 0.5 to 1.0 W/m²K, offering superior thermal resistance and energy savings.
Factors Affecting U-Value in Aluminum Doors

Let’s explore the key factors that contribute to better insulation and performance.
Frame Design and Thermal Breaks
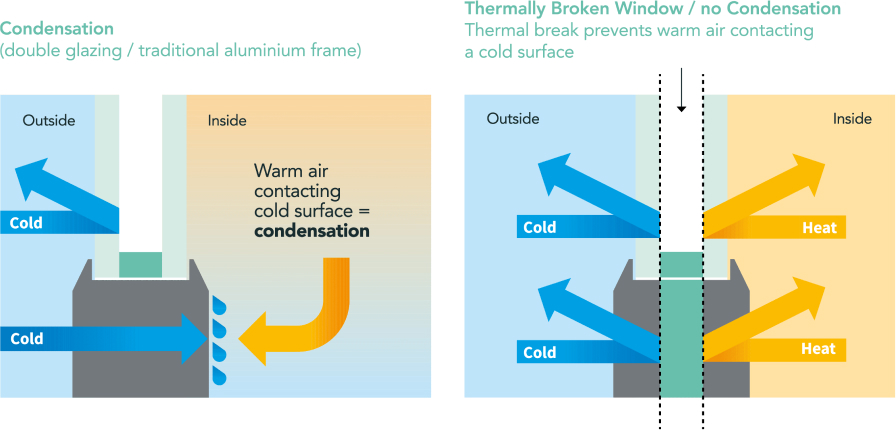
The addition of thermal breaks in the frame reduces heat transfer, improving U-value.Insulation and Core Materials
Insulation materials like foam and mineral wool enhance thermal resistance, lowering U-value.Glazing Options
Single, double, or triple glazing improves U-value, with Low-E glass boosting energy efficiency.Weatherstripping and Seals
Proper weatherstripping prevents air leakage, ensuring airtight performance and reducing energy loss.
How to Improve the U-Value of Existing Aluminum Doors
Here are some strategies to enhance thermal performance:
Upgrading to Thermally Broken Frames
Replacing old frames with thermally broken ones reduces heat transfer, lowering U-values and improving insulation.Adding Insulation to Existing Doors
Retrofitting with insulation materials like foam or mineral wool enhances thermal resistance, reducing energy consumption.Sealing Gaps and Replacing Weatherstripping
Replacing damaged seals and weatherstripping ensures airtightness, preventing heat loss and improving overall thermal performance.
How to Choose Aluminum Doors with Low U-Value

Here are some tips to help you make an informed decision:
Opt for Thermally Broken or Insulated Doors
These doors provide superior insulation by incorporating non-conductive materials or foam cores, significantly lowering the U-value.Look for High-Performance Glazing
Select doors with double or triple glazing and Low-E glass, which reduce heat transfer and improve energy efficiency.Consider the Climate
Choose doors with lower U-values if you live in colder climates to minimize heat loss and in hotter climates to prevent heat gain.
Conclusion
U-value plays a crucial role in aluminum doors, affecting insulation, energy efficiency, and comfort.
Lower U-values ensure better thermal performance, reducing energy costs and improving indoor conditions.
Choose aluminum doors with low U-values for enhanced energy efficiency.
Consult our experts to find the perfect door solutions for your needs and ensure professional installation. Contact us today!
FAQs About Aluminum Doors and U-Value
Are aluminium doors energy-efficient?
Yes, aluminum doors can be energy-efficient, especially when thermally broken or insulated. These designs minimize heat transfer and air leakage, which helps reduce heating and cooling costs, making them a smart investment for energy efficiency.
Can aluminium doors improve energy efficiency?
Absolutely! Aluminium doors with features like insulated cores, thermal breaks, and high-performance glazing significantly improve energy efficiency by preventing heat loss and gain, ultimately lowering utility bills.
What is the U-value of aluminum doors?
The U-value measures the heat transfer rate through a door. Standard aluminum doors have higher U-values, while thermally broken or insulated doors achieve much lower U-values, enhancing insulation and energy efficiency.

![U Value energy efficiency scale near a model house outdoors - Aluminum Door Panels U-Value: Key Insights [2026] - APRO U Value energy efficiency scale near a model house outdoors](https://aprowin.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/12/U-Value-energy-efficiency-scale-near-a-model-house-outdoors-2048x1152.webp)